G. Muñoz-Sanchez, M. Kalitsounaki, S. de Wit, K. Antoniadis, A.Z. Bonanos, E. Zapartas, K. Boutsia, E. Christodoulou, G. Maravelias, I. Soszynski, and A. Udalski
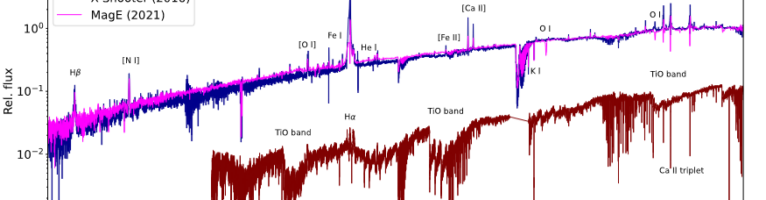
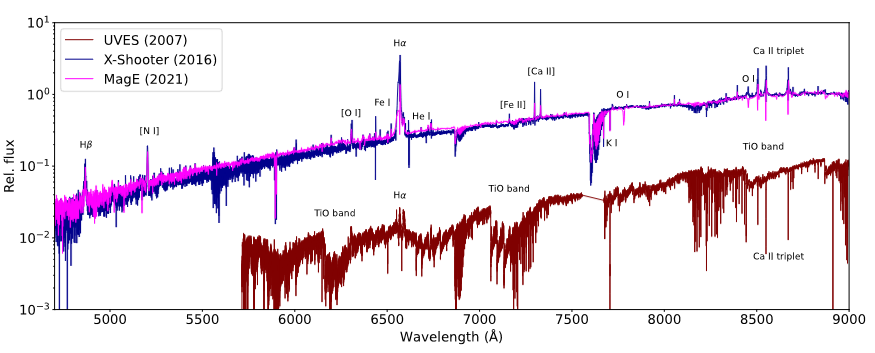
Red Supergiants (RSGs) are cool, evolved massive stars in the last evolutionary stage before exploding as a supernova. However, the most luminous RSGs may evolve blueward before exploding, given the observational evidence for luminous, warm, post-RSG objects and the lack of supernova progenitors originating from luminous RSGs. In this work, we analyze WOH G64, considered since the 1980s as the most extreme RSG in the Large Magellanic Cloud in terms of its size, luminosity, and mass-loss rate. Time-series photometry over the last 30 years reveals a sudden, yet smooth change from semi-regular to irregular variability in 2014. Multi-epoch optical spectroscopy confirms the transition, as WOH G64 now exhibits properties of a B[e] star in the optical, and warm-star features in the near-infrared. We report that WOH G64 has transitioned from a RSG to a Yellow Hypergiant and, moreover, has a B-star companion. The dramatic transition can be explained by: a) binary interactions partially stripping the envelope, b) the return of WOH G64 to a quiescent state after an outstanding eruption exceeding 30 years, and c) the expulsion of its outer layers due to a pre-SN superwind phase, indicating its imminent explosion. WOH G64 offers a unique opportunity to witness stellar evolution in real time, providing crucial clues for the late phases of massive stars and their resulting supernovae.
arXiv: 2411.19329 – Submitted to a high-impact journal