S. de Wit, A.Z. Bonanos, K. Antoniadis, E. Zapartas, A. Ruiz, N. Britavskiy, E. Christodoulou, K. De, G. Maravelias, G. Munoz-Sanchez, A. Tsopela
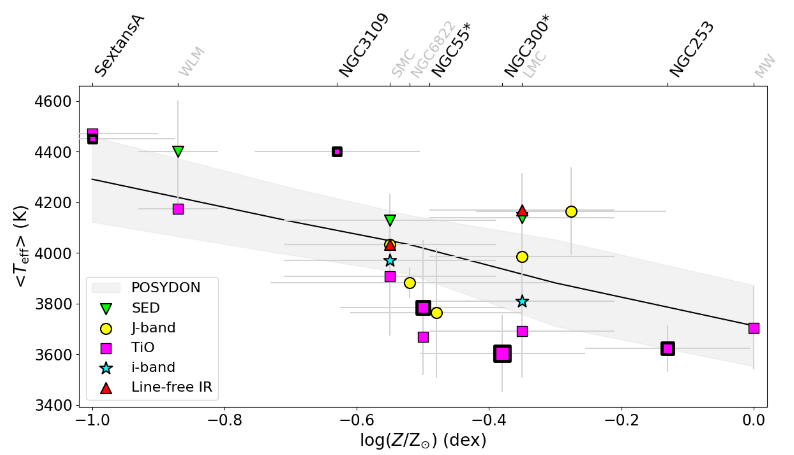
Mass loss during the red supergiant (RSG) phase plays a crucial role in the evolution of an intermediate massive star, however, the underlying mechanism remains unknown. We aim to increase the sample of well-characterized RSGs at subsolar metallicity, by deriving the physical properties of 127 RSGs in nine nearby, southern galaxies presented by Bonanos et al. For each RSG, we provide spectral types and used MARCS atmospheric models to measure stellar properties from their optical spectra, such as the effective temperature, extinction, and radial velocity. By fitting the spectral energy distribution, we obtained the stellar luminosity and radius for 97 RSGs, finding ∼50% with log(L/L⊙)≥5.0 and 6 RSGs with R≳1400 R⊙. We also find a correlation between the stellar luminosity and mid-IR excess of 33 dusty, variable sources. Three of these dusty RSGs have luminosities exceeding the revised Humphreys-Davidson limit. We then derive a metallicity-dependent J−Ks color versus temperature relation from synthetic photometry and two new empirical J−Ks color versus temperature relations calibrated on literature TiO and J-band temperatures. To scale our derived, cool TiO temperatures to values in agreement with the evolutionary tracks, we derive two linear scaling relations calibrated on J-band and i-band temperatures. We find that the TiO temperatures are more discrepant as a function of the mass-loss rate and discuss future prospects of the TiO bands as a mass-loss probe. Finally, we speculate that 3 hot, dusty RSGs may have experienced a recent mass ejection (12% of the K-type sample) and indicate them as candidate Levesque-Massey variables.